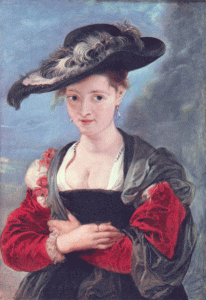ART IN MIDDLE AGES:
The medieval period began probably around 300 AD (when the Roman Empire fell) and ended around 1400 AD (when the period of Renaissance started). A large number of works in different mediums were prevalent in those times including sculptures, ceramic art, illuminated manuscripts, panel paintings, embroidery and tapestry art, stained glass, mosaics, fresco, metal work and engravings.



In the Early Middle Ages, the prevalent style of art was known as Byzantine Art. And the period was known as Dark ages. The drivers of this period were the authoritative people of the Eastern Orthodox Church. They financed most of the art works produced. Some significant works were very rare and were super costly. They were associated with the churches or monasteries, secular elites. During this period, decorative art such as enamel carving, embroidery were of much higher value than the usual paintings and monumental structures. Roman catacombs or burial crypts are those places where the oldest remains of Christian art have been found.


Public appreciation was the main purpose of creating artwork by the middle ages artists. They used classical themes at times. Like Christian scenery was depicted through Roman mosaics made of small pieces. Initially, these mosaics were made in muted colors but later the artists began using vibrant colors too.


The manuscripts during this time had luxuriously illuminated book-covers. Precious metals, ivory and gold adorned them. Even gold was in use very often. Churches, palaces, personal jewelry, mosaic backgrounds or miniatures in manuscripts or panel paintings were some of the things on which gold was found.

Summing up, a few characteristics of the Byzantine art were as follows:
- Art inspired by religion
- Artists were the members of religious houses like monasteries
- Sculptures were not prevalent
- Sombre tones were preferred
- There was no perspective in art, it was one dimensional
- Figures were usually front facing
- Realism was never portrayed
- Shadows were not made in any of the art form
FASHION IN MIDDLE AGES
Clothing during this period was influenced by the authorities. It reflected the social status of a person. Moreover, only the royal class could wear the fashionable attires prevalent in those times, ordinary people were not allowed to do so. Mostly, all the dresses were made of wool or any other thick and coarse material. These qualities gave the cloth strength and durability and were difficult to get ruined. If ruined, it was difficult to wash it.
Men’s Fashion:
Since the class of a person was the deciding factor for what clothes one would wear, two typical dresses for upper class men and the peasants is described below:


- Wealthy Men:
In early Middle Ages, a woolen tunic, belted at the waist, with embroidery at sleeves and hem was common among men. Over this, a woolen cloak was also worn which was fastened with a brooch.
In later period, velvet gown was in with a fur-trimmed hem. It was worn over a black padded shirt which had gold embroidery on it. In was short in length so they had to wear stockings to cover their legs. A hat was also worn to reflect their wealth and power in the society.
- Peasants:
Clothing of peasants or the lower class was always very basic and practical. In early middle Ages, they wore a short tunic over a short trouser. The tunic was as usual belted at the waist. A woolen cowl was also common and over it, a hat was also worn. They used to wear boots too.
Whereas, in the later period, instead of the trousers, stockings became more prevalent. And a woolen jacket became an addition on the tunic. They also wore a small hat.
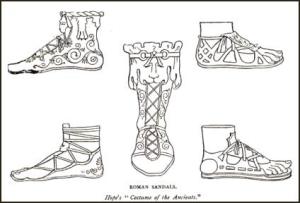
Additionally, men used to wear colored bands on their shoes, which were tied around the ankle and enhanced the shape of the foot.
Women’s Fashion:
The Greek and the Roman women were a huge inspiration for women during the middle ages. They used to wear tight clothing to reveal the elegance of their shape. They wore 2 tunics, out of which one was longer and the other shorter. Closed pointed shoes also became popular in those times


- Wealthy Women:
In the early middle ages, a white linen underskirt was worn, over which a woolen cloak was wrapped around. They also wore a linen headdress with a headband to keep it in place.
In the later period, women used to wear a woolen dress with fur-trimmed hem. The dress was belted at the waist. Fine expensive linen was used to make her headdress.
- Peasants:
In the early middle ages, they wore a woolen dress over a woolen underskirt. Along with this, shoes were worn and a cowl too, to protect her head and shoulders.
In the later period, same combination was prevalent. Moreover, a linen headdress also became popular.
Medieval Fashion gradually developed into shorter clothing for men and tighter clothing for women.
References:
- zeesonlinespace.net, (2014). History Of Fashion – Medieval. [online] Available at: http://fashionhistory.zeesonlinespace.net/medieval.html [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- com, (2014). Medieval Life – Clothing. [online] Available at: http://www.historyonthenet.com/medieval_life/clothing.htm [Accessed 21 Oct. 2014].
- Medieval-life-and-times.info, (2014). Medieval Clothing. [online] Available at: http://www.medieval-life-and-times.info/medieval-clothing/ [Accessed 21 Oct. 2014].
- org, (2014). Middle Ages Art. [online] Available at: http://www.lordsandladies.org/middle-ages-art.htm [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- net, (2014). Medieval Art and Art History. [online] Available at: http://www.arthistory.net/artstyles/medievalart/medievalart1.html [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- Wikipedia, (2014). Medieval art. [online] Available at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medieval_art [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- Alberge, D. (2013).East Anglian rood screens decaying as churches struggle for funds. [online] the Guardian. Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/culture/2013/dec/27/east-anglian-rood-screens-decay [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Encyclopedia Britannica, (2014).mosaic (art) :: Medieval mosaics in western Europe. [online] Available at: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/393310/mosaic/74117/Medieval-mosaics-in-western-Europe [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Mail Online, (2014).Holland Art Cities and how the Netherlands became one giant art gallery!. [online] Available at: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/travel/article-1173262/Holland-Art-Cities-Netherlands-giant-art-gallery.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- org, (2014).Pieta (Vesperbild) [Bohemian] (2001.78) | Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History | The Metropolitan Museum of Art. [online] Available at: http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/works-of-art/2001.78 [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- it, (2014).Rome Tours, Rome Sightseeing Tours, The Christian Catacombsof Rome. [online] Available at: https://www.travel.it/roma/hotelpanamagarden/en/hotel-rome-tour-4.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Wikipedia, (2014).Ravenna. [online] Available at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ravenna#mediaviewer/File:Meister_von_San_Vitale_in_Ravenna.jpg [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- co.uk, (2014).Collecting Sculpture in Early Modern Europe by Nicholas Penny – Yale University Press. [online] Available at: http://yalebooks.co.uk/display.asp?K=9780300121605# [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- com, (2014). Africa History And Photo Gallery. [online] Available at: http://www.reunionblackfamily.com/apps/photos/photo?photoid=154390036 [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Birthday in a Box, (2014). Mens Renaissance Costumes For Any Costume Party At Birthday In A Box. [online] Available at: http://www.birthdayinabox.com/costumes/mens-costumes/renaissance.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- English-online.at, (2014). Life in the Middle Ages | Clothing | Food | Health. [online] Available at: http://www.english-online.at/history/middle-ages/life-in-the-middle-ages.htm [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- History of Costume, (2011). Medieval Movies…and their Accuracy. [online] Available at: https://historyofeuropeanfashion.wordpress.com/2011/12/29/medieval-movies-and-their-accuracy/ [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- blogspot.in, (2011). All Things Historical Fiction: Fashion Throughout History (12th – 19th) Centuries. [online] Available at: http://allthingshistoricalfiction.blogspot.in/2011/05/fashion-throughout-history-12th-19th.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
ART IN MIDDLE AGES:
The medieval period began probably around 300 AD (when the Roman Empire fell) and ended around 1400 AD (when the period of Renaissance started). A large number of works in different mediums were prevalent in those times including sculptures, ceramic art, illuminated manuscripts, panel paintings, embroidery and tapestry art, stained glass, mosaics, fresco, metal work and engravings.
In the Early Middle Ages, the prevalent style of art was known as Byzantine Art. And the period was known as Dark ages. The drivers of this period were the authoritative people of the Eastern Orthodox Church. They financed most of the art works produced. Some significant works were very rare and were super costly. They were associated with the churches or monasteries, secular elites. During this period, decorative art such as enamel carving, embroidery were of much higher value than the usual paintings and monumental structures. Roman catacombs or burial crypts are those places where the oldest remains of Christian art have been found.
Public appreciation was the main purpose of creating artwork by the middle ages artists. They used classical themes at times. Like Christian scenery was depicted through Roman mosaics made of small pieces. Initially, these mosaics were made in muted colors but later the artists began using vibrant colors too.
The manuscripts during this time had luxuriously illuminated book-covers. Precious metals, ivory and gold adorned them. Even gold was in use very often. Churches, palaces, personal jewelry, mosaic backgrounds or miniatures in manuscripts or panel paintings were some of the things on which gold was found.
Summing up, a few characteristics of the Byzantine art were as follows:
- Art inspired by religion
- Artists were the members of religious houses like monasteries
- Sculptures were not prevalent
- Sombre tones were preferred
- There was no perspective in art, it was one dimensional
- Figures were usually front facing
- Realism was never portrayed
- Shadows were not made in any of the art form
FASHION IN MIDDLE AGES
Clothing during this period was influenced by the authorities. It reflected the social status of a person. Moreover, only the royal class could wear the fashionable attires prevalent in those times, ordinary people were not allowed to do so. Mostly, all the dresses were made of wool or any other thick and coarse material. These qualities gave the cloth strength and durability and were difficult to get ruined. If ruined, it was difficult to wash it.
Men’s Fashion:
Since the class of a person was the deciding factor for what clothes one would wear, two typical dresses for upper class men and the peasants is described below:
- Wealthy Men:
In early Middle Ages, a woolen tunic, belted at the waist, with embroidery at sleeves and hem was common among men. Over this, a woolen cloak was also worn which was fastened with a brooch.
In later period, velvet gown was in with a fur-trimmed hem. It was worn over a black padded shirt which had gold embroidery on it. In was short in length so they had to wear stockings to cover their legs. A hat was also worn to reflect their wealth and power in the society.
- Peasants:
Clothing of peasants or the lower class was always very basic and practical. In early middle Ages, they wore a short tunic over a short trouser. The tunic was as usual belted at the waist. A woolen cowl was also common and over it, a hat was also worn. They used to wear boots too.
Whereas, in the later period, instead of the trousers, stockings became more prevalent. And a woolen jacket became an addition on the tunic. They also wore a small hat.
Additionally, men used to wear colored bands on their shoes, which were tied around the ankle and enhanced the shape of the foot.
Women’s Fashion:
The Greek and the Roman women were a huge inspiration for women during the middle ages. They used to wear tight clothing to reveal the elegance of their shape. They wore 2 tunics, out of which one was longer and the other shorter. Closed pointed shoes also became popular in those times.
- Wealthy Women:
In the early middle ages, a white linen underskirt was worn, over which a woolen cloak was wrapped around. They also wore a linen headdress with a headband to keep it in place.
In the later period, women used to wear a woolen dress with fur-trimmed hem. The dress was belted at the waist. Fine expensive linen was used to make her headdress.
- Peasants:
In the early middle ages, they wore a woolen dress over a woolen underskirt. Along with this, shoes were worn and a cowl too, to protect her head and shoulders.
In the later period, same combination was prevalent. Moreover, a linen headdress also became popular.
Medieval Fashion gradually developed into shorter clothing for men and tighter clothing for women.
References:
- zeesonlinespace.net, (2014). History Of Fashion – Medieval. [online] Available at: http://fashionhistory.zeesonlinespace.net/medieval.html [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- com, (2014). Medieval Life – Clothing. [online] Available at: http://www.historyonthenet.com/medieval_life/clothing.htm [Accessed 21 Oct. 2014].
- Medieval-life-and-times.info, (2014). Medieval Clothing. [online] Available at: http://www.medieval-life-and-times.info/medieval-clothing/ [Accessed 21 Oct. 2014].
- org, (2014). Middle Ages Art. [online] Available at: http://www.lordsandladies.org/middle-ages-art.htm [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- net, (2014). Medieval Art and Art History. [online] Available at: http://www.arthistory.net/artstyles/medievalart/medievalart1.html [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- Wikipedia, (2014). Medieval art. [online] Available at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medieval_art [Accessed 1 Nov. 2014].
- Alberge, D. (2013).East Anglian rood screens decaying as churches struggle for funds. [online] the Guardian. Available at: http://www.theguardian.com/culture/2013/dec/27/east-anglian-rood-screens-decay [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Encyclopedia Britannica, (2014).mosaic (art) :: Medieval mosaics in western Europe. [online] Available at: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/393310/mosaic/74117/Medieval-mosaics-in-western-Europe [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Mail Online, (2014).Holland Art Cities and how the Netherlands became one giant art gallery!. [online] Available at: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/travel/article-1173262/Holland-Art-Cities-Netherlands-giant-art-gallery.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- org, (2014).Pieta (Vesperbild) [Bohemian] (2001.78) | Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History | The Metropolitan Museum of Art. [online] Available at: http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/works-of-art/2001.78 [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- it, (2014).Rome Tours, Rome Sightseeing Tours, The Christian Catacombsof Rome. [online] Available at: https://www.travel.it/roma/hotelpanamagarden/en/hotel-rome-tour-4.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Wikipedia, (2014).Ravenna. [online] Available at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ravenna#mediaviewer/File:Meister_von_San_Vitale_in_Ravenna.jpg [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- co.uk, (2014).Collecting Sculpture in Early Modern Europe by Nicholas Penny – Yale University Press. [online] Available at: http://yalebooks.co.uk/display.asp?K=9780300121605# [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- com, (2014). Africa History And Photo Gallery. [online] Available at: http://www.reunionblackfamily.com/apps/photos/photo?photoid=154390036 [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- Birthday in a Box, (2014). Mens Renaissance Costumes For Any Costume Party At Birthday In A Box. [online] Available at: http://www.birthdayinabox.com/costumes/mens-costumes/renaissance.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- English-online.at, (2014). Life in the Middle Ages | Clothing | Food | Health. [online] Available at: http://www.english-online.at/history/middle-ages/life-in-the-middle-ages.htm [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- History of Costume, (2011). Medieval Movies…and their Accuracy. [online] Available at: https://historyofeuropeanfashion.wordpress.com/2011/12/29/medieval-movies-and-their-accuracy/ [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].
- blogspot.in, (2011). All Things Historical Fiction: Fashion Throughout History (12th – 19th) Centuries. [online] Available at: http://allthingshistoricalfiction.blogspot.in/2011/05/fashion-throughout-history-12th-19th.html [Accessed 27 Nov. 2014].